Same-Same-Same Test (SSS)
The purpose of the Same-Same-Same test (SSS) and the Same-Same-Different test (SSD) IDEAScripts are to identify abnormal duplications as potential indicators of errors or fraud.
Updated Sept 17, 2015 - Updated the dialog.
IDEAScript
The Same-Same-Same Test (SSS)
and
The Same-Same-Different Test (SSD)
The purpose of the Same-Same-Same test (SSS) and the Same-Same-Different test (SSD) IDEAScripts are to identify abnormal duplications as potential indicators of errors or fraud.
These tests are based on chapter 12 of Mark J. Nigrini’s book, entitled, “Forensic Analytics: Methods and Techniques for Forensic Accounting Investigations”. [1]
The Same-Same-Same Test (SSS)
This test identifies records which contain fields of information that are exact duplicates of other records. The user may select up to 8 fields to match.
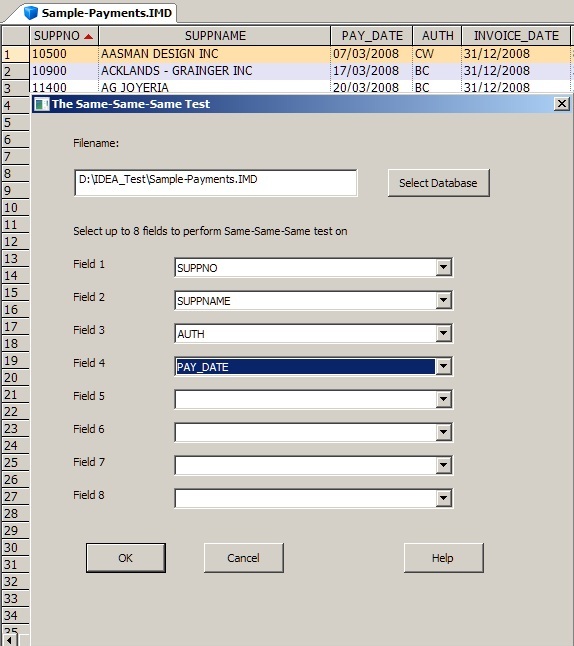
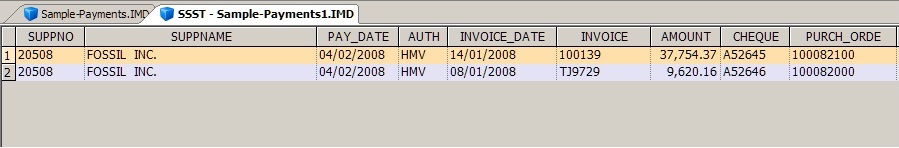
Application of this test will assist in detecting duplicate expenses claimed, occurrences of the same payment to vendors made in error, multiple warranty claims or duplicated service fees paid by private or government health plans.
The Same-Same-Different Test (SSD)
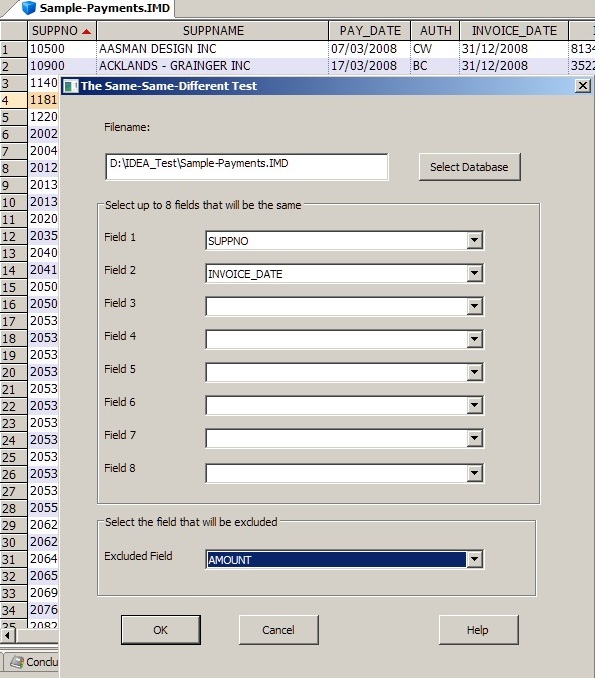
This test is used to identify records with near duplicates for fields selected by the users. The user may select up to 8 fields to match and one field that is excluded from the matching.
Note that for IDEA Versions 8.5 and prior, when applying Duplicate Key Exclusion manually, incorrect output results where there are duplicate field contents for the selected exclusion field. This SSD IDEAScript produces the correct output.
In chapter 12 of Dr. Mark Nigirini’s Forensic Analytics book, he states, “The same-same-different test is a powerful test for errors and fraud. This test should be considered for every forensic analytics project.” His experience has shown that, “This test always detects errors in accounts payable data” and “The longer the time period, the higher the chances of SSD detecting errors”.
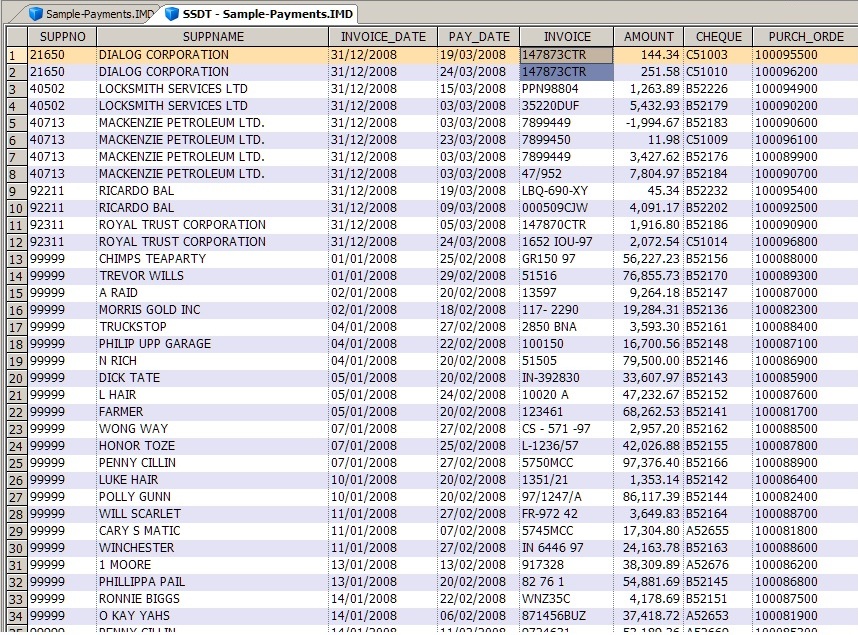
One such example which demonstrates the value of this test is in the detection of instances where a payment is made to a wrong vendor initially and then subsequently the correct vendor is properly paid (same invoice number, same amount, and different vendors).
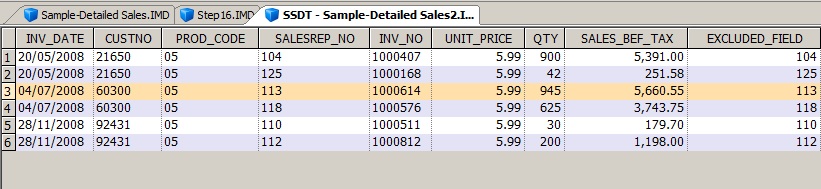
If a business system does not process orders in real time, the above example may indicate customers attempting to split their orders to avoid exceeding their credit limit (same invoice date, same customer number, same product code, and different sales representatives).
[1] Nigrini, Mark J., Forensic Analytics: Methods and Techniques for Forensic Accounting Investigations, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011: Print

Compile error
Version 10.1.3.5
Error on line 3 - Compile error:
Syntax error
Line 3 is -> Begin Dialog dlgSSSTest 50,40,273,255,"The Same-Same-Same Test", .displayIt
'dlgSSSTest' is highlighted after clicking OK of the error message window.
Thank you, in advance. ~Mark